BMI Height Weight Chart : Ideal Weight for Men and Women | Health Benefits and Risks
-
Introduction
- Understanding the Importance of Ideal Weight
- Overview of Height-Weight Charts
-
Ideal Weight Chart According to Height for Men and Women
- Ideal Height Weight Chart for Men
- Ideal Height Weight Chart for Women
- Ideal Body Measurements for Men Based on Height
-
Body Fat Percentage Table for Men and Women
- Understanding Body Composition and Health
- Health Implications of Body Fat Percentage
-
Average/Healthy Weight and Weight Categories
- Defining Healthy Weight Ranges
- Underweight Category: Risks and Concerns
- Overweight Category: Health Risks and Management
-
Understanding Body Mass Index (BMI)
- Formula to Calculate BMI
- How to Use the BMI Formula
- Interpreting BMI Results
- Example Calculation
-
Why Height-Weight Chart for Men and Women Is Useful?
- Assessing Health Status
- Identifying Malnutrition and Obesity
- Importance in Public Health Initiatives
-
Factors Affecting Ideal Weight
- Age
- Gender
- Muscle vs. Fat Composition
- Genetic Factors
-
Health Risks of Being Underweight and Overweight
- Risks Associated with Low Body Weight
- Health Consequences of Excess Body Weight
-
Achieving and Maintaining Ideal Weight
- Strategies for Healthy Weight Management
- Adopting a Holistic Approach to Health and Wellness
-
Height-Weight Chart FAQs
- Answers to Common Questions about Height-Weight Charts, BMI, and Health
Overview
The ideal weight chart according to height for both men and women serves as a fundamental tool in assessing and understanding body weight in relation to height. It provides guidelines for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight range, thereby promoting overall health and well-being. Additionally, understanding body mass index (BMI) further aids in evaluating weight status and potential health risks. Let's delve into each aspect in detail.
The ideal weight chart serves as a foundational guide for individuals striving to attain optimal health and well-being. Tailored specifically to gender and height, this chart offers a comprehensive range of weights that individuals should aim to achieve in order to maintain a healthy lifestyle. For men, the chart provides a spectrum of ideal weights corresponding to various heights, enabling them to assess their weight status and take proactive measures to achieve optimal health. Similarly, the chart for women offers a range of ideal weights based on height, empowering women to gauge their weight in relation to their height and make informed decisions regarding their health and fitness goals. By providing tangible benchmarks for weight management, the ideal weight chart serves as a roadmap for individuals embarking on their journey towards better health.
In addition to weight, body measurements such as chest, waist, and hips play a crucial role in assessing body composition and overall health. These measurements offer valuable insights into an individual's physique and can help identify areas for improvement. For men, ideal body measurements based on height provide a framework for achieving balanced proportions and muscular development. By striving to attain ideal measurements, men can work towards a physique that not only looks aesthetically pleasing but also promotes optimal health and functionality. Whether aiming to increase muscle mass or reduce excess body fat, understanding ideal body measurements serves as a valuable tool in guiding fitness and nutrition goals.
Body fat percentage is another key metric that contributes to a comprehensive assessment of body composition. By measuring the proportion of body fat relative to lean muscle mass, individuals can gain insights into their overall health status and identify potential areas for improvement. The body fat percentage table for both men and women delineates healthy ranges of body fat percentage, providing individuals with a benchmark for evaluating their own body composition. By striving to maintain a healthy body fat percentage, individuals can reduce their risk of obesity-related health conditions and promote overall well-being. Whether through dietary modifications, exercise, or lifestyle changes, achieving and maintaining a healthy body fat percentage is essential for optimizing health and longevity.
Understanding body mass index (BMI) is integral to assessing weight status and identifying potential health risks. BMI is a widely used measure that calculates an individual's body fat based on their weight and height. By using the BMI formula, individuals can determine their BMI and interpret the results to assess their weight status. BMI falls within specific ranges, including underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obesity, each of which corresponds to different health implications. By understanding their BMI and its implications, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain a healthy weight and reduce their risk of obesity-related health conditions.
Ideal Height Weight Chart for Men and Women
The ideal height weight chart for both men and women serves as a cornerstone in the pursuit of optimal health and well-being. Tailored to gender-specific physiological differences and varying heights, these charts provide individuals with tangible guidelines for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight range. Let's explore each chart in detail, highlighting the recommended weight ranges based on height.
Ideal Height Weight Chart for Men:
|
Height (ft-in/cm) |
Ideal Weight Range (kg) |
Ideal Weight Range (lbs) |
|
5’0″/152 cm |
58 – 71 |
128 – 156 |
|
5’1″/155 cm |
59 – 73 |
131 – 160 |
|
5’2″/157 cm |
60 – 74 |
133 – 163 |
|
5’3″/160 cm |
62 – 75 |
136 – 166 |
|
5’4″/163 cm |
63 – 77 |
139 – 169 |
|
5’5″/165 cm |
64 – 78 |
142 – 173 |
|
5’6″/168 cm |
66 – 80 |
145 – 177 |
|
5’7″/170 cm |
68 – 83 |
149 – 182 |
|
5’8″/173 cm |
69 – 84 |
152 – 186 |
|
5’9″/175 cm |
70 – 86 |
155 – 190 |
|
5’10″/178 cm |
72 – 88 |
159 – 194 |
|
5’11″/180 cm |
74 – 90 |
162 – 198 |
|
6’0″/183 cm |
75 – 92 |
166 – 202 |
|
6’1″/185 cm |
77 – 94 |
169 – 207 |
|
6’2″/188 cm |
78 – 96 |
173 – 211 |
|
6’3″/191 cm |
80 – 98 |
176 – 216 |
|
6’4″/193 cm |
82 – 100 |
180 – 220 |
Ideal Height Weight Chart for Women:
|
Height (ft-in/cm) |
Ideal Weight Range (kg) |
Ideal Weight Range (lbs) |
|
5’0″/152 cm |
47 – 58 |
104 – 127 |
|
5’1″/155 cm |
48 – 59 |
106 – 130 |
|
5’2″/157 cm |
49 – 60 |
108 – 132 |
|
5’3″/160 cm |
50 – 61 |
111 – 135 |
|
5’4″/163 cm |
52 – 63 |
114 – 138 |
|
5’5″/165 cm |
53 – 64 |
117 – 142 |
|
5’6″/168 cm |
54 – 66 |
120 – 146 |
|
5’7″/170 cm |
56 – 68 |
123 – 150 |
|
5’8″/173 cm |
57 – 70 |
126 – 154 |
|
5’9″/175 cm |
59 – 72 |
129 – 158 |
|
5’10″/178 cm |
60 – 74 |
132 – 162 |
|
5’11″/180 cm |
61 – 75 |
135 – 166 |
|
6’0″/183 cm |
63 – 77 |
138 – 170 |
|
6’1″/185 cm |
64 – 79 |
141 – 174 |
|
6’2″/188 cm |
65 – 81 |
144 – 178 |
|
6’3″/191 cm |
67 – 83 |
147 – 182 |
|
6’4″/193 cm |
68 – 84 |
150 – 186 |
These charts offer individuals a tangible reference point for assessing their weight status and setting realistic health goals. By comparing their current weight to the recommended weight ranges based on height, individuals can identify areas for improvement and take proactive steps towards achieving optimal health and well-being. Additionally, these charts serve as valuable tools for healthcare professionals in guiding their patients towards healthier lifestyle choices and weight management strategies.
Body Fat Percentage Table for Men and Women
Body fat percentage is a critical component of body composition that influences overall health and well-being. Understanding and maintaining healthy body fat levels is essential for reducing the risk of obesity-related health conditions and promoting optimal health. The body fat percentage table for both men and women delineates healthy ranges of body fat percentage, providing individuals with a benchmark for evaluating their own body composition.
Body Fat Percentage Table for Men:
|
Body Fat Percentage |
Description |
|
Essential Fat |
2-5% |
|
Athletes |
6-13% |
|
Fitness |
14-17% |
|
Average |
18-24% |
|
Obese |
25% and above |
Body Fat Percentage Table for Women:
|
Body Fat Percentage |
Description |
|
Essential Fat |
10-13% |
|
Athletes |
14-20% |
|
Fitness |
21-24% |
|
Average |
25-31% |
|
Obese |
32% and above |
These tables provide individuals with a clear understanding of healthy body fat ranges based on gender. By assessing their body fat percentage and comparing it to the recommended ranges, individuals can gauge their overall health status and take proactive steps towards achieving optimal body composition. Additionally, healthcare professionals can utilize these tables to guide their patients in developing personalized nutrition and fitness plans aimed at optimizing body composition and promoting overall well-being.
Average/Healthy Weight
Maintaining an average or healthy weight is paramount for overall health and well-being. Falling within the healthy weight range indicates that an individual is at a lower risk for obesity-related health conditions and is more likely to enjoy a higher quality of life. The average/healthy weight category serves as a benchmark for individuals striving to achieve and maintain optimal health through balanced nutrition and regular physical activity.
Underweight Category
Being underweight poses significant health risks and can lead to various complications, including nutrient deficiencies, weakened immune system, and increased susceptibility to infections. Individuals classified as underweight may experience symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and poor concentration. It is essential for underweight individuals to consult with a healthcare professional to identify the underlying causes of their low weight and develop a comprehensive treatment plan to achieve a healthy weight range.
Overweight Category
Being overweight increases the risk of developing a wide range of health conditions, including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers. Excess weight can also impact quality of life, leading to decreased mobility, joint pain, and reduced self-esteem. Individuals classified as overweight should work towards achieving a healthy weight range through lifestyle modifications such as adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and seeking support from healthcare professionals or weight management programs.
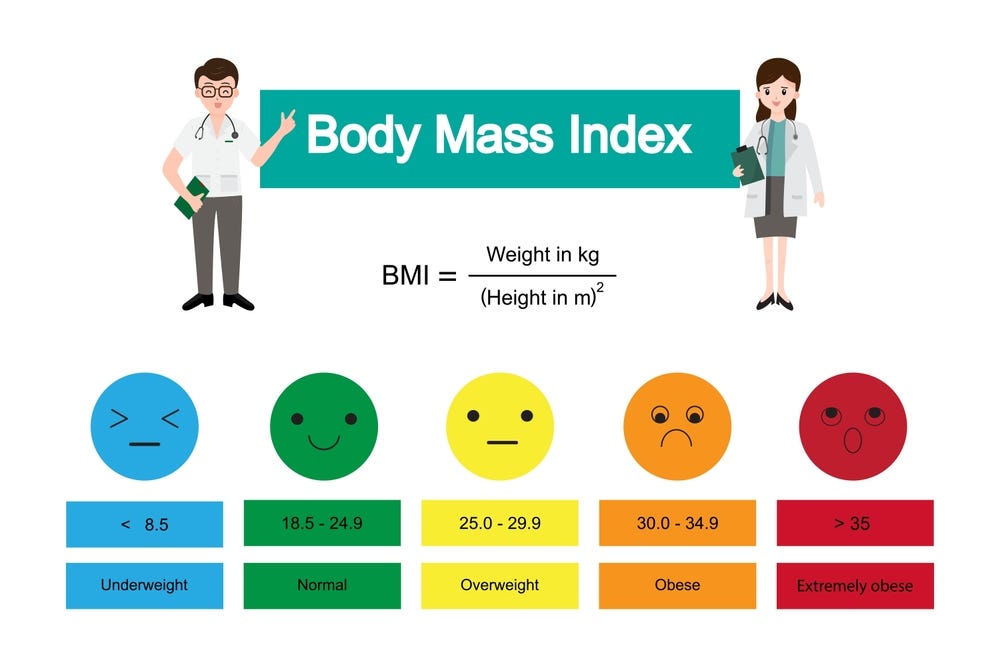
Understanding Body Mass Index (BMI)
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used measurement tool to assess an individual's body weight relative to their height. It provides a numerical value that categorizes individuals into different weight status categories, such as underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obesity. BMI serves as a screening tool to identify potential weight-related health risks and is often used by healthcare professionals to guide clinical assessments and interventions.
Formula to Calculate BMI
The formula to calculate BMI is relatively straightforward and involves dividing an individual's weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. The mathematical expression for calculating BMI can be expressed as follows:
For Metric Measurements: BMI = Weight in Kilograms / (Height in Meters)²
For Imperial Measurements: BMI = Weight in Pounds / (Height in Inches)² * 703
How to Use the BMI Formula
Utilizing the BMI formula is a simple process that involves obtaining accurate measurements of an individual's weight and height and applying them to the appropriate formula based on the chosen unit of measurement (metric or imperial). Once the BMI value is calculated, it can be interpreted to determine the individual's weight status category.
Interpret the Result:
The interpretation of BMI values involves categorizing individuals into different weight status categories based on established cutoff points. The World Health Organization (WHO) provides standard BMI categories as follows:
- Underweight: BMI less than 18.5
- Normal weight: BMI 18.5–24.9
- Overweight: BMI 25–29.9
- Obesity: BMI 30 or more
Example Calculation:
Let's consider an example to illustrate the calculation of BMI:
Suppose an individual weighs 70 kilograms and has a height of 1.75 meters. The BMI calculation would be as follows:
- BMI = Weight in Kilograms / (Height in Meters)²
- BMI = 70 / (1.75)²
- BMI = 70 / 3.0625
- BMI ≈ 22.86
Based on this calculation, the individual's BMI falls within the "Normal weight" range, indicating that their weight is considered healthy relative to their height.
By applying the BMI formula and interpreting the results, individuals and healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into an individual's weight status and potential health risks associated with excess or insufficient body weight. However, it's important to note that while BMI is a useful screening tool, it does have limitations and should be interpreted in conjunction with other clinical assessments for a comprehensive evaluation of an individual's health status.
Why Height-Weight Chart For Men and Women Is Useful?
Height-weight charts for men and women serve as invaluable tools for various aspects of health management and promotion. They offer a range of benefits, making them essential resources in healthcare, fitness, and public health initiatives.
Assessing Your Health
One of the primary uses of height-weight charts is to assess an individual's overall health status. By comparing their weight to their height, individuals can determine whether they fall within a healthy weight range. This assessment can provide valuable insights into potential health risks associated with being underweight, overweight, or obese, allowing individuals to take proactive steps towards improving their health.
Identify Malnutrition
Height-weight charts also play a crucial role in identifying malnutrition and nutritional deficiencies. Individuals who fall below the recommended weight range for their height may be at risk of malnutrition, which can have serious implications for their overall health and well-being. By recognizing deviations from the healthy weight range, healthcare professionals can intervene early to address nutritional deficiencies and prevent further complications.
Detect Obesity
Similarly, height-weight charts help in the early detection of obesity, a significant risk factor for numerous chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Individuals whose weight exceeds the recommended range for their height may be classified as overweight or obese, prompting further evaluation and intervention to mitigate associated health risks. Height-weight charts provide a simple yet effective method for identifying individuals who may benefit from weight management strategies.
Easily Understandable
One of the key advantages of height-weight charts is their simplicity and ease of use. Unlike more complex measurements such as body fat percentage or waist circumference, height-weight charts provide a straightforward visual representation of an individual's weight relative to their height. This simplicity makes them accessible to a wide range of individuals, including those with limited health literacy, facilitating greater awareness and understanding of weight-related health risks.
Personalized Health Guide
Height-weight charts can also serve as personalized health guides, helping individuals set realistic weight management goals based on their unique characteristics. By identifying their current weight status relative to their height, individuals can determine whether they need to maintain, lose, or gain weight to achieve optimal health. This personalized approach empowers individuals to take control of their health and make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and lifestyle habits.
Useful for Public Initiatives
Height-weight charts are invaluable tools for informing public health initiatives aimed at promoting healthy weight management and preventing obesity-related diseases. By providing standardized guidelines for assessing weight status, height-weight charts enable policymakers, healthcare providers, and community organizations to develop targeted interventions and education campaigns. These initiatives can help raise awareness about the importance of maintaining a healthy weight and provide resources and support for individuals looking to improve their health.
Factors Affecting Ideal Weight
Several factors can influence an individual's ideal weight and their placement on a height-weight chart. These factors include:
- Age: Body composition and metabolic rate can change with age, impacting an individual's weight distribution and overall health.
- Gender: Biological differences between males and females, such as muscle mass and fat distribution, can influence ideal weight ranges.
- Muscle vs. Fat: Muscle tissue is denser than fat tissue, meaning that individuals with higher muscle mass may weigh more while still falling within a healthy weight range.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic predispositions can influence an individual's metabolism, body shape, and propensity for weight gain or loss, contributing to variations in ideal weight among individuals.
Health Risks of Being Under the Ideal Weight
Being under the ideal weight range can pose significant health risks and complications. Individuals who fall below the recommended weight for their height may experience various adverse effects on their physical and mental well-being. Some of the health risks associated with being under the ideal weight include:
- Malnutrition: Underweight individuals often have inadequate nutrient intake, which can lead to malnutrition. Malnutrition deprives the body of essential vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients, impairing overall health and increasing susceptibility to infections and illnesses.
- Weakened Immune System: Malnutrition and insufficient calorie intake can weaken the immune system, making underweight individuals more vulnerable to infections, illnesses, and prolonged recovery times.
- Increased Risk of Osteoporosis: Low body weight can lead to decreased bone density and increased risk of osteoporosis, a condition characterized by fragile and brittle bones. This heightened risk of fractures and bone injuries can significantly impact mobility and quality of life.
- Fertility Issues: Women who are underweight may experience disruptions in their menstrual cycles, including irregular periods or the absence of menstruation (amenorrhea). These menstrual irregularities can affect fertility and increase the risk of reproductive health issues.
- Impaired Wound Healing: Underweight individuals may experience delays in wound healing and recovery following injuries or surgical procedures. Malnutrition and inadequate nutrient intake can compromise the body's ability to repair tissues and regenerate cells, leading to slower healing times and increased susceptibility to infections.
- Decreased Muscle Mass: Chronic undernutrition and low body weight can result in muscle wasting and decreased muscle mass. This loss of muscle tissue can impair physical strength, endurance, and functional abilities, affecting overall mobility and independence.
Health Risks of Being Overweight
Being overweight or obese significantly increases the risk of developing various chronic health conditions and complications. Excess body weight, particularly visceral fat around organs, contributes to metabolic dysfunction and inflammation, predisposing individuals to numerous health risks. Some of the health risks associated with being overweight include:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Overweight individuals are at increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension (high blood pressure), atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), coronary artery disease, and stroke. Excess body fat can lead to elevated cholesterol levels, increased blood pressure, and impaired cardiovascular function, contributing to heart disease and related complications.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Obesity is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes, a metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and elevated blood sugar levels. Excess adipose tissue, particularly visceral fat, disrupts insulin signaling and glucose metabolism, leading to insulin resistance and diabetes development.
- Joint Pain and Osteoarthritis: Excess body weight places additional stress on weight-bearing joints, such as the knees, hips, and lower back, increasing the risk of joint pain, inflammation, and osteoarthritis. Obesity-related joint problems can impair mobility, reduce quality of life, and necessitate medical interventions such as joint replacement surgery.
- Sleep Apnea: Obesity is a common risk factor for obstructive sleep apnea, a sleep disorder characterized by repetitive episodes of breathing cessation during sleep. Excess adipose tissue in the neck and throat can obstruct the airway, leading to breathing difficulties, snoring, daytime fatigue, and increased cardiovascular strain.
- Fatty Liver Disease: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a prevalent liver disorder associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome. Accumulation of excess fat in the liver can lead to inflammation, liver damage, and progression to more severe conditions such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cirrhosis.
- Cancer: Obesity is linked to an increased risk of several types of cancer, including breast, colorectal, pancreatic, liver, and kidney cancer. Adipose tissue produces hormones and inflammatory substances that promote tumor growth and metastasis, contributing to cancer development and progression.
Achieving and Maintaining Ideal Weight
Achieving and maintaining an ideal weight is essential for optimizing health and reducing the risk of weight-related complications. Several strategies can help individuals reach and maintain a healthy weight range:
- Balanced Diet: Focus on consuming a balanced diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. Avoid excessive consumption of processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-calorie snacks, opting instead for nutrient-dense, portion-controlled meals.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise and physical activity to support weight management, improve cardiovascular health, and enhance overall fitness. Incorporate a combination of aerobic exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises into your routine to promote calorie burning, muscle development, and metabolic health.
- Behavioral Modifications: Adopt healthy lifestyle habits and behaviors to support long-term weight management goals. Practice mindful eating, portion control, stress management techniques, and adequate sleep hygiene to foster a balanced and sustainable approach to weight loss and maintenance.
- Medical Monitoring: Consult with healthcare professionals, such as physicians, dietitians, and fitness experts, for personalized guidance and support in achieving ideal weight goals. Regular medical check-ups, monitoring of body composition, and assessments of metabolic health can help track progress and identify any underlying issues that may impact weight management efforts.
Adopt A Holistic Approach To Health And Wellness
In addition to focusing on achieving and maintaining an ideal weight, individuals should adopt a holistic approach to health and wellness that encompasses physical, mental, and emotional well-being. A holistic approach emphasizes the interconnectedness of various aspects of health and promotes strategies for promoting overall wellness. Some key components of a holistic approach to health and wellness include:
- Nutrition: Prioritize nutrient-dense, whole foods and balanced meals to nourish the body and support optimal health. Pay attention to portion sizes, meal timing, and mindful eating practices to cultivate a healthy relationship with food and promote sustainable dietary habits.
- Physical Activity: Incorporate regular exercise and physical activity into your daily routine to improve fitness, enhance cardiovascular health, and manage weight. Choose activities that you enjoy and that align with your fitness goals, whether it's walking, cycling, yoga, or strength training.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, mindfulness, or relaxation techniques to alleviate stress and promote mental well-being. Managing stress is essential for maintaining hormonal balance, reducing inflammation, and supporting overall health.
- Sleep Hygiene: Prioritize quality sleep and establish healthy sleep habits to support physical and mental recovery, hormone regulation, and cognitive function. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night and create a relaxing sleep environment free of distractions.
- Social Connection: Cultivate meaningful relationships and social connections with family, friends, and community members to foster a sense of belonging, support, and emotional well-being. Engage in activities that promote social interaction, collaboration, and mutual support.
- Mind-Body Practices: Explore mind-body practices such as yoga, tai chi, qigong, or meditation to promote relaxation, mindfulness, and self-awareness. These practices can help reduce stress, improve mental clarity, and enhance emotional resilience.
Height Weight Chart FAQs
What is an Ideal Height Weight Chart?
An ideal height weight chart is a reference tool used to determine a range of healthy weights based on an individual's height. It provides guidelines for assessing whether a person's weight falls within a healthy range relative to their height.
How is Ideal Weight Determined for Men and Women?
Ideal weight is determined for men and women based on various factors, including height, age, gender, body composition, and overall health. Formulas take into account physiological differences between men and women, as well as muscle mass distribution and fat distribution patterns.
Does Age Affect Ideal Weight?
Yes, age can affect ideal weight, as metabolism and body composition change over time. Ideal weight may vary depending on factors such as muscle mass, bone density, and hormonal changes associated with aging.
Why Do Ideal Weight Ranges Vary Between Ethnic Groups?
Ideal weight ranges may vary between ethnic groups due to genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Genetic differences can influence metabolism, fat distribution, and body composition, while environmental factors such as diet and physical activity levels also play a role.
How Should I Use the Height Weight Chart?
The height weight chart should be used as a guide for assessing weight health. Individuals can compare their weight to the recommended range for their height and gender to determine whether they fall within a healthy weight range.
Are There Different Charts for Adults and Children?
Yes, there are different height weight charts for adults and children. Children's charts take into account growth and development factors, while adult charts focus on maintaining a healthy weight range.
Can Muscle Mass Affect My Position on the Chart?
Yes, muscle mass can affect an individual's position on the height weight chart. Muscular individuals may have a higher weight due to greater muscle mass, but this does not necessarily indicate poor health, as muscle is denser than fat.
Is BMI a Reliable Indicator of Healthy Weight?
BMI (Body Mass Index) offers a basic assessment of weight health but does not differentiate between muscle, fat, and bone mass. While BMI can provide a general indication of weight status, it may not be accurate for individuals with high muscle mass or specific body compositions.
How Often Should I Check My Weight Against the Chart?
It is recommended to check your weight against the height weight chart periodically, such as during routine medical check-ups or when monitoring changes in weight over time. However, weight should not be the sole determinant of health, and other factors such as body composition and overall well-being should also be considered.
Can the Height Weight Chart Help with Weight Loss Goals?
Yes, the height weight chart can be a useful tool for setting realistic weight loss goals and tracking progress over time. By comparing current weight to the recommended range for height and gender, individuals can establish achievable targets for reaching and maintaining a healthy weight.




